Definition. Meaning:
The
common English meaning of the word is devaluation or reduction in the value of
an asset. This fall in value may be for many reasons including normal wear and
tear, fall in market price and so on. However in accounting/ financial parlance
the word depreciation is used in the sense of normal wear and tear of fixed
assets on account of use and time.
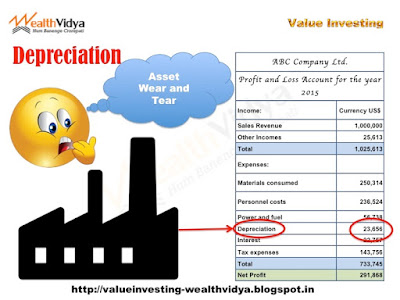
Depreciation
is treated as an expense every year while computing the profits and drawing up
the ‘Profit & Loss Account’ of a business.
 |
| Picture showing depreciation of factory assets due to normal wear and tear |
Methods of Calculation:
Depreciation
is calculated usually under two methods:
- Straight-line: The residual value of the asset is written off equally over the useful life of the asset. Results in uniform charge throughout.
- Written Down Value: At the end of every year the depreciation charged during the year is reduced from the value of the asset (written down value). In the next year the depreciation rate is applied on the written down value. Results in higher depreciation in the initial years and lower charge in latter periods.
Conclusion:
Depreciation
is an expense arising out of normal wear and tear of fixed assets due to use
and passage of time. It is charged off as an expense every year in the profit
and loss statement.