While investing it is best to convert everything into ‘per
share’.
Why?
Because we, retail investors, are not buying whole companies
but only small portions of companies through their shares. Many times retail
investors only buy a few shares of a company. Sometimes even only one. So
understanding various company aspects at the per-share level makes a lot
of sense.
Therefore many important aspects like earnings, book value,
cash flow are reduced to the single share level. As a result we have:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): Net Profit of the company reduced to a single share.
- Book Value Per Share: Total Book Value of the company reduced to the individual share.
- Face Value of a Share: The equity capital of a company is divided into a certain number of units or shares of a certain small value to make it easy to sell and raise the capital. This basic unit value - without ant premium or discount - is called the face value. For example the equity capital of a small private company of Rs.100000 is divided into 10000 shares of Rs.10 each. This Rs.10 per share is called the face value.
Once we have these per-share information in hand, we can
make even more important price-value comparisons, like:
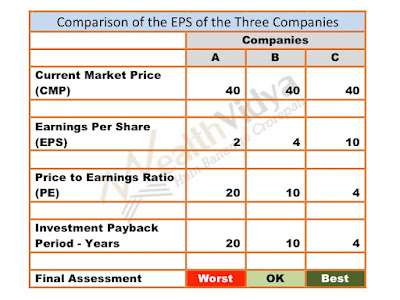
- Price to Earnings (PE) Patio: Measures how many times the earnings we are paying as premium or looking from a different angle, in how many years the investment is earned back.
- Price to Book Value (P2BV) Ratio: Indicates how many times the book value we are paying as price or at what discount to the book value is the share available currently in the market.
Why these ratios are important?
Value Investing prescribes certain wise thumb
rules for making stock buying like:
- PE Ratio shall not be more than 15. Lower the positive PE number so much better it is.
- The P2BV ratio shall not be more than 1.5. Lower the positive number it is, so much better.
- The product or combination of these two ratios shall not be more than 22.5.
You can learn more details in the following related
articles:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS) - Definition
- Definition of Price to Earnings (PE) Ratio
- Definition of Book Value per Share